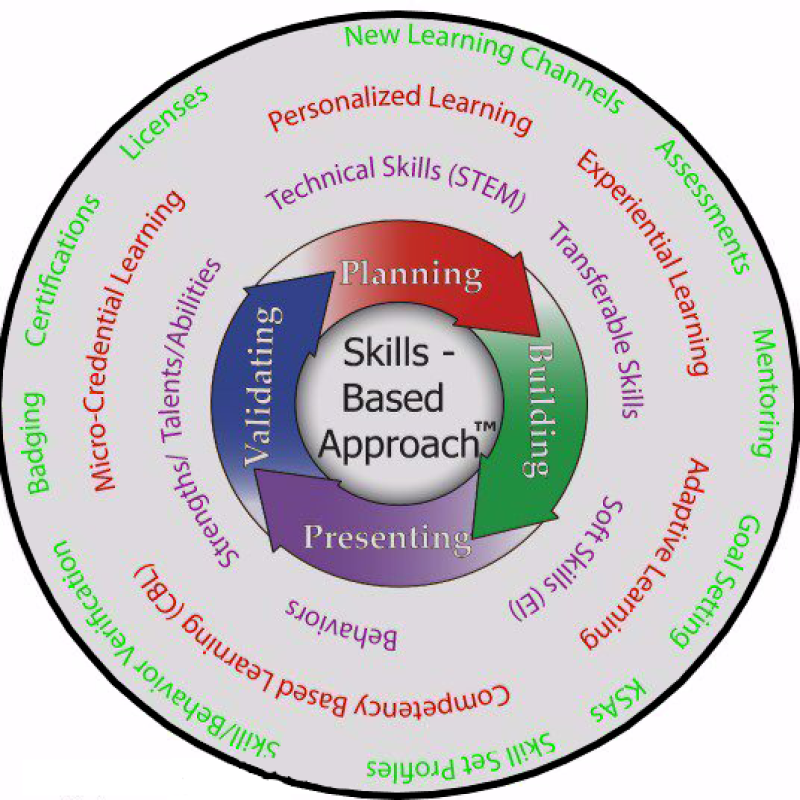
Many of the latest learning trends fit well with Skills-Based Approach, which is valuable because of the huge simplification of the methodology. Learners and practitioners at any age can grasp moving through and the general mechanics of the four stages. These are how some of the latest learning trends work with Skills-Based Approach:
Skills are finally getting the attention they deserve. Practitioners are not only expressing technical skills, but also transferable, soft, and thinking skills – taking an all-encompassing tactic. The evidence is with the number of large open source and proprietary ‘skills databases’ being built in the past five years (as referenced earlier); one such database is claimed to have thirty thousand skills.
As technology gets better, instructors can craft personalized learning for their learners in a time reasonable way. One good example is with the Skill Label system, which supports personalized learning in three ways (learners): choose their assignments; move through a series based on performance; and get personal lesson plans. Skills-Based Approach is designed as a ‘learner centric’ application, where learners participate in decision making and are always aware of precisely each task, objective, or credential they are working on.
Experiential learning is widely touted as a way to improve poor learner engagement and provide a deeper, lasting effect. Skills-Based Approach targets this type of learning by inherently focusing so strongly on skills.
Competency Based Learning (CBL) started gaining traction in 2014 as a different model for learning, where learners are tested for reaching desired skill achievements (competencies) and get ‘credit’ when accurately assessed. This is different than our current time-based curriculum, which is rooted in five-month semesters and a credit hours system. CBL programs benefit all participants: underperforming learners get extra help; average learners move at their own pace; and overachieving students get to keep moving forward. Given the recent COVID crisis, moving to a CBL framework might alleviate some of the structural education and higher education problems. To conceptualize how CBL works with Skills Based Approach, think of the graphic as a dynamic, constantly spinning cycle, where it is possible to change the speed to move faster or slower. Furthermore, each learner gets his or her own cycle.
Micro-Credentialing is gaining acceptance as training institutions recognize learners have a decreasing attention span and get their learning content on mobile devices. Practitioners can target skill gains in three to five-minute spurts. Now imagine spinning through Skills Based Approach daily.
There are a number of new learning channels being considered in mainstream education, higher education and training; some of them include: online and console games, virtual reality experiences, quick and long videos, and online interactive classrooms. Skills-Based Approach does not differentiate. Use any learning resource in the planning and building stages to optimize learning and connect the expectations together by describing them in skills.
The first edition of this book accurately predicted the rise of badges and certifications. The driving forces behind each of them are: creating shorter, more effective learning paths and increasing requirement for lifelong learning. Responses to the COVID crisis illustrates both of them well. First, there are skills initiatives where we are trying to get workers back to work in the most expediate way (the skills renewal act). Second, a common tagline in social media is signaling taking a class and receiving a certification while working from home.
Skills-Based Approach suggests constructing a validation strategy to select the best way to verify skills, so works wells with the traditional and emerging ways to validate skills. And repeatedly cycling through the validation stage is ideal for the re- skilling and upskilling demands of the modern worker.